04-Expansion_Pins_Testing
This document is used for users to quickly use or test the expansion pin functions of the motherboard.
Symbol Explanation
SDK$: Refers to the source code path.console$: Generally refers to the command-line console of the motherboard. Motherboard command-line consoleADB$: Android Debug Bridge command-line tool, generally refers to an environment where ADB can be run.
Expansion Pins
The development board is equipped with on-board expansion pin functions.
It can be used to connect external devices (such as temperature sensors, humidity sensors, etc.).
Communicate with other circuit boards or modules (I2C, SPI, UART, etc.).
Customize GPIO functions.
For specific function expansion details, refer to the pin list.
The pin list marks the default configuration of each pin (marked with an asterisk) and provides the available alternative configurations for that pin.
K7 Expansion Pin List
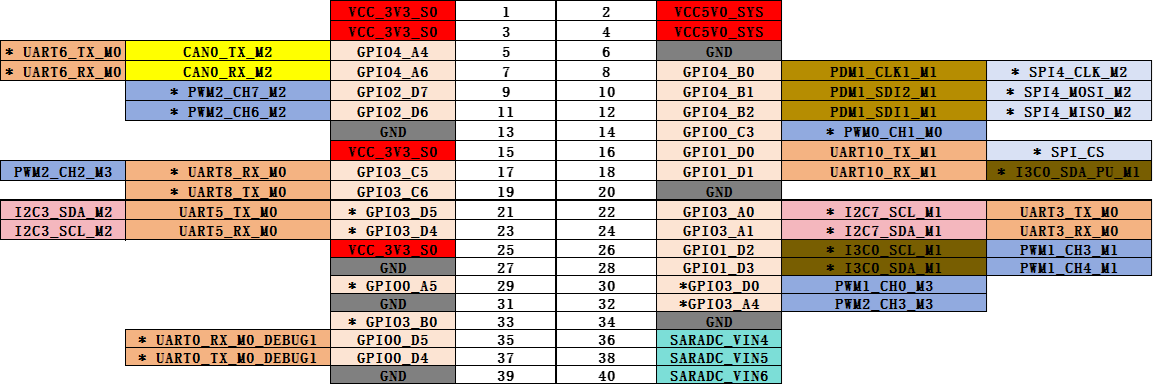
K7 Pin Voltage

GPIO
The expansion pins of the K7 motherboard can be configured as GPIO pins. Check the corresponding GPIO pin positions and numbers in the Expansion Pins section.
The default GPIO pins (marked with an asterisk) of the expansion pins are configured as output ports, which can control the GPIO to output high or low levels.
List the registered GPIO control nodes
To control the level state of the GPIO below, $GPIO needs to correspond to the listed GPIO names.
Control the output level state of the GPIO
Control the GPIO to output a high level
Control the GPIO to output a low level
Example:
Control GPIO3_D4 to output a high level
Control GPIO3_D4 to output a low level
CAN
The expansion pins of the K7 motherboard can be configured as CAN interfaces. Check the corresponding CAN interface positions and numbers in the Expansion Pins section.
Query the current CAN device
The following uses CAN0 as an example for illustration.
It can be seen that the device name is can0.
Configure CAN
Turn off CAN
Set the arbitration segment to a 1M baud rate and the data segment to a 3M baud rate
View the configuration information of can0
Start CAN
CAN Transmission
Transmit (standard frame, data frame, ID: 123, data: DEADBEEF)
Transmit (extended frame, data frame, ID: 00000123, data: DEADBEEF)
CAN Reception
Enable printing and wait for reception
Loopback Mode Test
In loopback mode, the data sent by cansend can be received by candump.
PWM
The expansion pins of the K7 motherboard can be configured as PWM interfaces. Check the corresponding PWM positions and channel numbers in the Expansion Pins section.
List the PWM nodes
List the corresponding PWM DTS nodes
The corresponding relationships are as follows, from top to bottom, corresponding to pwmchip0 to pwmchip2.
PWM0_CH1_M0 - pwm0_2ch_1 - pwm@27331000 - pwmchip0
PWM2_CH6_M2 - pwm2_8ch_6 - pwm@2ade6000 - pwmchip1
PWM2_CH7_M2 - pwm2_8ch_7 - pwm@2ade7000 - pwmchip2
Configure PWM
Example:
The software has already configured PWM0_CH1_M0 (marked with an asterisk) by default. The following uses PWM0_CH1_M0 for illustration.
Set the PWM0_CH1_M0 channel, corresponding to pwmchip0, with a period of 10000ns, a duty cycle of 5000ns, and a polarity of normal.
After successful configuration, you can use a multimeter to measure the PWM0_CH1_M0 pin, and the voltage should be around 1.6V.
UART
The expansion pins of the K7 motherboard can be configured as UART interfaces. Check the corresponding UART positions and channel numbers in the Expansion Pins section.
Loopback Test
The software has already configured UART8 by default. The following uses UART8 as an example for illustration.
Short-circuit RX and TX hardware.
Use microcom to specify UART8 for communication
Example:
In the loopback test, microcom can receive the output characters simultaneously.
SPI
The expansion pins of the K7 motherboard can be configured as SPI interfaces. Check the corresponding SPI positions and channel numbers in the Expansion Pins section.
Loopback Test
The software has already configured SPI4 by default. The following uses SPI4 as an example for illustration.
Short-circuit MISO and MOSI hardware.

List the SPI device nodes
Specify the device for testing
Example:
The tool's network disk path
3-SoftwareData\Linux_Spi_Tool\spidev_test
ADC
The expansion pins of the K7 motherboard are equipped with three ADC channels. Check the corresponding ADC positions and channel numbers in the Expansion Pins section.
Read the ADC value
Example:
Read the voltage value of channel 4
Last updated