03-Functional_Testing
This document aims to help users quickly get started or test the functions of the motherboard's peripheral interfaces.
LED
There are 2 LED indicators on the motherboard:
Green LED: Power indicator. It remains constantly lit by default after power-on.
Blue LED: System heartbeat indicator. If this light flashes continuously, it indicates that the kernel is running normally.

KEY
The motherboard is equipped with four buttons with the following functions:
LOADER Button
During system startup: Used as a programming button.
When the system is running normally: Can be configured as any button as required.

RESET Button
System reset button. Pressing this button resets the system.

POWER Button
Power button, used to control the power switch of the motherboard.

MASKROM Button
The Maskrom mode is the initial state of the system when the firmware is not programmed or the firmware data is cleared. This button is usually used for system repair when the bootloader is damaged, such as flashing new firmware, unlocking the device, or rescuing a bricked device.

Ethernet
The motherboard is equipped with two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. After connecting the network cable, the motherboard will automatically obtain an IP address and connect to the network.

USB
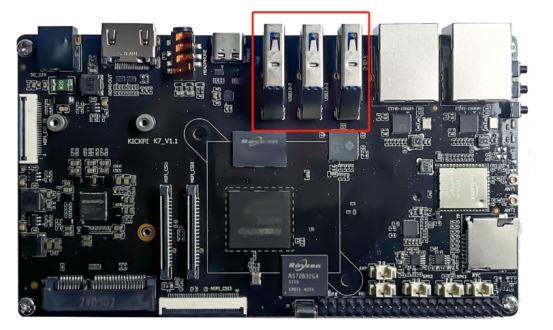
USB Type A (1 - 3)
The motherboard has three USB 3.0 TYPE - A interfaces, supporting HOST mode. They can be connected to common USB peripherals such as mice, keyboards, cameras, and docking stations.
USB Type C
The motherboard is equipped with one USB 3.0 TYPE - C interface with the following features:
Supports automatic mode recognition and switching.
Supports HOST mode, allowing connection to USB peripherals such as mice, keyboards, cameras, and docking stations.
Supports DEVICE mode, enabling functions such as adb.
Supports DP v1.4 display output.

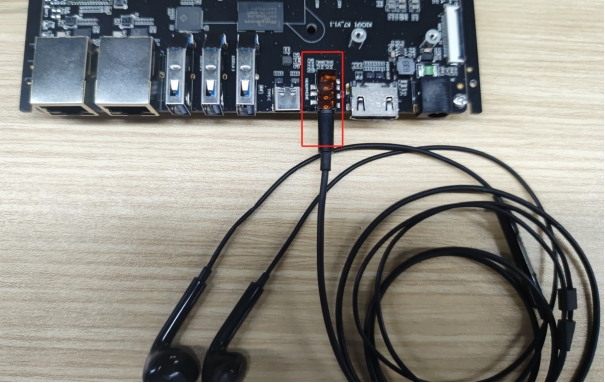
Headphone
The motherboard is equipped with one 3.5mm headphone jack.
Hardware Wiring
LCD
See Quick Start for details.
4G/5G
The motherboard is equipped with one MINI - PCIE interface, which can be connected to 4G/5G modules. The compatible modules are as follows:
EC20
4G
EC200
4G
RG200U
5G
Hardware Wiring
Wiring for connecting the motherboard to a 4G or 5G mobile network module via MINI-PCIE.

Inserting a SIM card into the motherboard.

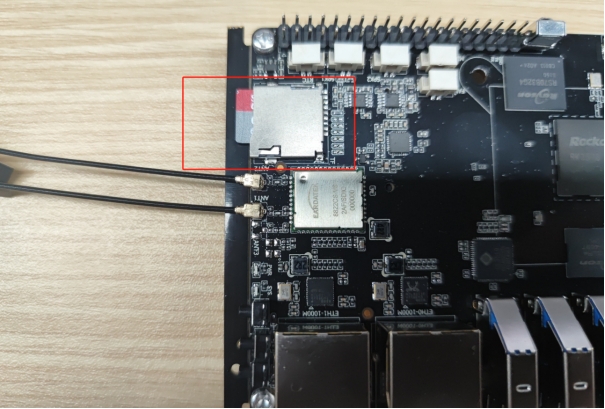
SD Card
The motherboard is equipped with one Micro SD Card interface, which can be connected to an SD memory card for file read and write operations.
Hardware Wiring
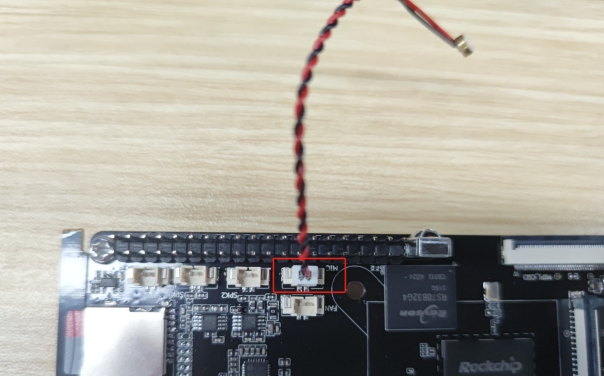
IR
The motherboard supports infrared remote control and is compatible with the KICKPI remote control by default.
KICKPI Remote Control

Infrared Remote Control Receiver

WIFI
An onboard 8822CS module is provided.

BT
An onboard 8822CS module is provided.

MIC
The motherboard is equipped with one MIC interface, which can be connected to a MIC microphone for recording.
Hardware Wiring
Speaker
The motherboard is equipped with two speaker interfaces, supporting audio output for left and right channel speakers.
Hardware Wiring

RTC
The motherboard has an onboard RTC module hym8563 and is equipped with one RTC battery interface. After connecting the battery, the RTC can continue to work using the battery when the motherboard loses power.
Hardware Wiring

Test steps:
Connect the development board to the network to automatically synchronize the correct network time.
Disconnect the network connection and the power supply of the development board.
After waiting for some time, reconnect the power supply of the development board.
If the system time is consistent with the current time, the RTC function is normal.
FAN
The motherboard is equipped with one fan interface. The fan is turned on by default after power-on.
Hardware Wiring
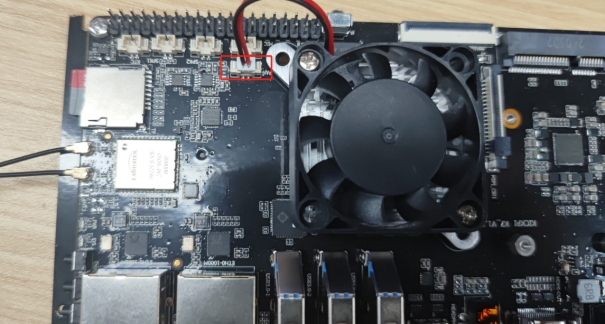
Switch Control
Turn on the fan
Turn off the fan
M.2 SSD
The motherboard is equipped with one PCIE 2.0 M.2 SSD hard drive interface, which can be connected to a hard drive for file read and write operations.
Hardware Wiring

MPP
Debug Information
Enable debug information
After enabling debug information, there will be log information similar to the following when calling hardware encoding and decoding. [ 893.134037] rk_vcodec: 27b00100.rkvdec:0 session 3705:19 time: 1333 us hw 1312 us [ 893.167444] rk_vcodec: 27b00100.rkvdec:0 session 3705:19 time: 1381 us hw 1313 us [ 893.200503] rk_vcodec: 27b00100.rkvdec:0 session 3705:19 time: 1420 us hw 1313 us
Disable debug information
Debian / Ubuntu
Rockchip provides MPP-related tools for use.
Hardware Encoding Test
mpi_enc_test
Encoding test for 100 frames of H.264 4096x2160
View the results
$ tail -f /var/log/syslog
kickpi mpp[3557]: mpi_enc_test: chn 0 encode 100 frames time 3763 ms delay 27 ms fps 26.57 bps 10605252
Encoding test for 100 frames of H.265 4096x2160
View the results
$ tail -f /var/log/syslog
kickpi mpp[3560]: mpi_enc_test: chn 0 encode 100 frames time 4086 ms delay 36 ms fps 24.47 bps 19594276
Hardware Decoding Test
mpi_dec_test
Decoding test for 100 frames of H.264 4096x2160
View the results
$ tail -f /var/log/syslog
kickpi mpp[3564]: mpi_dec_test: decode 100 frames time 596 ms delay 25 ms fps 167.53
Decoding test for 100 frames of H.265 4096x2160
View the results
$ tail -f /var/log/syslog
kickpi mpp[3569]: mpi_dec_test: decode 100 frames time 803 ms delay 49 ms fps 124.47
Chromium Video Test
Connect the board to a display device, open a virtual terminal or a debug serial terminal, and execute the following command to start the Chromium video test.
There is a compatibility issue with hardware decoding configuration between Rockchip Chromium and GStreamer in Ubuntu!
Chromium is configured for use by default. If Chromium does not call hardware decoding, use the following command to fix it.
After configuration, Chromium can call hardware decoding by default.
GStreamer Video Test
If there are signs of MPP calls, it means the hardware decoding is successfully called.
There is a compatibility issue with hardware decoding configuration between Rockchip Chromium and GStreamer in Ubuntu!
Chromium is configured for use by default. If you need GStreamer to call hardware decoding, use the following command to fix it.
This command requires an internet connection to ensure 'apt update' succeeds.
After configuration, GStreamer can call hardware decoding by default.
NPU
Debian / Ubuntu
Rockchip provides NPU test scripts.
NPU frequency test script npu_freq_scaling.sh
Example: Run the NPU with frequency changes for 60 seconds, changing the frequency every 10 seconds.
NPU stress test script npu_stress_test.sh
The content after
Begin perf...shows the performance data of multiple model runs:
Each record shows the run number, the corresponding elapsed time (
Elapse Time), and the frames per second (FPS). For example,0: Elapse Time = 2.85ms, FPS = 351.12means that during the first model inference run, it took a total of 2.85 milliseconds, and from this, it can be calculated that 351.12 frames of data can be processed per second (the FPS is calculated by dividing 1000 by the elapsed time for each run, and then converting the unit to frames per second).The
---- Top5 ----section presents the top 5 categories with the highest probabilities in the model inference output results, along with their corresponding probability values and category numbers:
0.935059 - 156means that the model believes the input data (such as an image) is most likely to belong to category number 156, with a corresponding probability as high as 0.935059. This relatively high probability value indicates that the model has a relatively high confidence in this judgment.The subsequent
0.057037 - 155,0.003881 - 205,0.003119 - 284, and0.000172 - 285list the category numbers and probability values of the second to fifth most probable categories respectively. These probability values decrease successively, indicating that the model's confidence in their belonging to the corresponding categories also gradually decreases.
GPU
Check GPU Utilization
Example: Check the utilization in real-time
$ watch -n 1 'cat /sys/devices/platform/*gpu/utilisation'
Move the mouse or drag the window to check the GPU utilization to determine if hardware acceleration is working.
GLmark2 Performance Test
Rockchip provides GPU test scripts.
Last updated